
Fish like there is a tomorrow - fish safe.
A web site for the Commercial Fishing Vessel Industry
Here is a central location to find NVICs, instructions, regulations, policy letters, policy decisions and reference material related to the commercial fishing vessel safety program.
Report any broken links to michael.g.rudolph@uscg.mil
This section also provides interpretation or additional guidance on some topics.
- Alphabetical listing of topics
- 105 Exams - Fish Processing Vessels Dispensing Petroleum Products
- 46 USC 3702 fish processing vessels less than 5000GT that dispense petroleum products are required to comply with 46 CFR 105 be examined in accordance with the Part 105 Inspection Checklist and required to be issued a Part 105 Letter . According to 46 USC 3702 (c) - Fishing and Fish Tender vessels of not more than 500GT are not required to comply with this requirement
Fish processing vessels 5000GT and greater are required to be inspected and certificated under the Coast Guard vessel inspection program.
The primary purpose of a fishing, fish tender or fish processing vessel is not the dispensing of petroleum products. The Coast Guard's position is that if a vessels carries combustable or flammable liquids in bulk either Marine Portable Tanks (MPT's) or independant tanks and carries more than 20 percent of its DWT it is operating as a tank vessel and must be certificate under Subchapter D. Generally, a vessel carrying less than 20 percent of its DWT is not deemed to be principally carrying bulk combustible or flammable cargo. The Part 105 Inspection Checklist refers to the Marine Safety Manual (MSM) Volume II Chapter 11.F. This is the old MSM and an excerpt is provided for reference.
D17 provided policy for conducting "courtesy" 105 exams of fishing and fish tender vessels less than 500GT. See D17's policy dated 28 Aug 1995
- This is a copy, for historcial purposes, of the Notice of Proposed Rule Making (NPRM) posted Aug 20th 2014 and the Final Rule posted Mar 1, 2016 both in the federal register that makes changes to 46 CFR 105.
- 3rd Party Examiners
- NVIC 13-91 - Dated October 7, 1991 this provided initial policy for 3rd party organizations and established criteria for "accepted organizations" and "similarly qualified organizations".
- NVIC 13-91 Change 1 - Dated Apr 28, 1993 revises methods for distribution of decals and expands scope of volutanry dockside exams..
- MOC Policy Ltr 04-07 - Dated Aug 6, 2007 provided additional guidance on the acceptance of accepted organization and similarly qualified organizations and provided for rescinding of acceptance of an individual third party qualification. This guidance also stipulates that all exam paperwork be submitted to the Area Coordinators as opposed to District as outlined in 46 CFR 28.710(e).
- CVC-WI-019(1) - Origination Date Aug 1, 2019 Commercial Fishing Vessel (CFV) Third Party Examination Program and Procedures for Designation as an Accepted Organization or Similarly Qualified Organization - This Work Instruction clarifies and consolidates existing Coast Guard Commercial Fishing Vessel Safety (CFVS) Program requirements related to dockside safety examinations and Third Parties that conduct such examinations.
- List of 3rd party examiner organizations accepted by the Coast Guard - These organization are authorized to conduct dockside examinations of commercial fishing vessels and to issue decals to satisfy the mandatory dockside exam requirements.
- 13th (Northwest) District Waters guidance
- Deviations of Boundary Line in Northwest District. 46 CFR 7.140 & 7.145 - There are 4 locations in the Northwest District where the boundary line deviates from the general definition.
- 13th District Boundary Line Message P170126Z FEB 94 - Provides a simplified location for the boundary line for the Puget Sound applicable to enforcement. The boundary line is a line drawn north from Angeles Point. This is also a 13th District Ltr dated 14 July 92 with same definition.
- Coastal Water Definition - 33 CFR 175.105
- Cold Waters - NVIC 7-91 - All waters in the Northwest District are cold waters
- Navigable Waters of the Northwest District - Excerpt from the Northwest District SOP.
- ADF&G Alaska Vessel Registraion Number Marking System
- ADF&G Vessel Registration Number Marking - 5 AAC 39.119 - The Alaska Department of Fish and Game requires that the vessel registration number assigned to a commercial fishing vessel be marked on the vessels as follows. Markings shall be at least 12 inches in height and 1 inch in width that contrasts with the background. Visible on both sides of the hull, cabin or mast. Plainly visible and unobscured..
- Alaska Fishing Vessels Transporting Cargo
- Alaska Fishing Vessels Transporting Cargo
- Normally vessels that carry cargo for hire are required to be inspected 46 USC 3302 exempts fishing, fish tender and fish processing vessels that carry cargo to Alaska ports that do not receive weekly service from inspected cargo vessels from having to be inspected. They may not transport cargo to ports that do receive weekly cargo service by inspected cargo vessels. The Aleutian Trade Act (ATA) provides a special exemption to this regulation (see ATA Vessels below)- Alaska Youth Worker Laws - Alaska law prohibits minors under age 16 from working on a fishing boat UNLESS the boat is operated by a parent.
- Aleutian Trade Act (ATA) Vessels
- - this act allows vessels within specific boundaries (from mid Kodiak Island to the western most island (Attu)) in Alaska to carry cargo to remote locations that receive weekly common carrier service by certificated cargo vessels such as Sealand and Crowley
- Aleutian Trade Act of 1990
- Congressional Record October 27, 1990 - - House discussion on implementation of the Aleutian Trade and list of the original 20 vessels.
- 46 USC 2102 - Definition of Aleutian Trade.
- Map of Aleutian Trade area - the area is west of 153 degrees west longitude and east of 172 degrees east longitude.
- Supplementary Notice of Proposedl Rule - Federal Register - October 27, 1992 - This SNPRM was proposed after some of the items in the Final Rule of August 14, 1991 generated comments of public concern and were separated from the final rule in order that the items could be adequately be addressed. These topic include stability for fishing vessels < 79 feet, survivall craft requirements carrying less than 4 POB inside 12 miles. Also Aleutian Trade Act, Load Lines, drill course curricula and instructor acceptance criteria, termination of fishing vessels.
- Correction Notice of Proposedl Rule - Federal Register - January 6, 1993 - This includes corrections to SNPRM of October 27, 1992.
- Supplementary Notice of Proposedl Rule - Federal Register - September 13, 1994 - Aleutian Trade Act Vessels. Establishes proposed regulations which would allow some commercial fishing vessels to continued to proivde cargo service to remote communities in Alaska.
- Final Rule - Federal Register - October 24, 1995 - Aleutian Trade Act Vessels. New vessels are allowed to enter the trade but are required to comply with 46 CFR Part 28 subpart D.
- 46 USC 3302 - In the 2006 Coast Guard and Maritime Transportation Act of 2006, 46 US Code 3302(3)(B) was changed to state .A fish tender vessel of not more than 500 gross tons as measured under section 14502 of this title, or less than 500 gross tons as measured under section 14502 of this title, or is less than 2,500 gross tons as measured under section 14302 of this title, which is qualified to engage in the Aleutian trade is exempt from section 3301 (1), (6), and (7). (An ATA vessel if under 2,500 gross international tons is exempted from inspection).
- CG-5587 Checklist ATA Addendum - Addendum checklist for Aleutian Trade Act Fish Tenders.
- Anti Fouling Paint
- Anti Fouling Paint - Policy - CG-CVC Policy Ltr 12-08 dated Oct 15, 2012
- Anti Fouling Paint - IMO Resolution
- Automatic Identification Systems (AIS) -Required for all self propelled commercial fishing vessels, tenders and processor greater than 65 feet in length.
- WHAT IS AIS?
- AIS transmits data to the AIS system. All vessels in the system are presented on a screen providing the user with a picture of other vessels relative to the users vessel. By selecting a vessel on the screen the user is presented with information about that vessel including the vessels name, course, speed, classification, call sign, registration number and other important information about the vessel. This information is also provided to the Coast Guard in order to track vessels entering the United States.

- WHO IS REQUIRED TO HAVE AIS?
- AIS is required for all self propelled commercial fishing vessels, fish tender vessel and fish processing vessels that are 65 feet or greater are required to have installed either a Class A or Class B (AIS) in accordance with (33 CFR 164.46(b)(1)(i)). If you have questions please refer to the USCG Navigation Center website.
- AIS must remain in continuous operation at all times while the vessel is operating.
- AIS may be switched off if continuous operation would compromise safety or security of the vessel. This action and the reason for taking it must be reported to the nearest U.S. Captain of the Port or Vessel Traffic Center and recorded in the ship's logbook. The AIS should return to continuous operation as soon as the source of danger has been mitigated.
- Auxiliary Coast Guard Personnel Conducting Dockside Exams
- HQ Policy Letter 06-04. - Dated July 19, 2006 this policy provides guidance for qualification and travel related to utilizing Coast Guard Auxiliary examiners for the commercial fishing vessel safety program.
- CG543 Policy Letter 12-02- Dated March 1, 2012 - Final policy that states that Coast Guard Auxiliary personnel may assist the CFIVS program by conducting mandatory dockside exams as proviided for with the signing of the Coast Guard Authorization Act of 2010.
- Battery Replacement (scheduled maintenance Table 28.140)
- NVIC 1-92 (Enclosure 5) - Regular batteries sold over the counter such as 9 volt and A, C or D cells even though they have a date must be replaced annually. Special marine type battereis marked with an expiration date must be replaced after the date marked on the battery.
- Bilge Alarms
- 46 CFR 28.250 - This is to clarify that there must be a visual alarm indicator located at the primary operating station for each space fitted with a high water alarms alarm. Each separate space must provide its own indication by a separate visual indicator. Unlike the visual alarm, all high water indicators can be tied to the same audible alarm. If a space such as an engine room has two high level indicators fitted in the same space they may both illuminate the same visual indicator.
............- Boarding Ladder
- 50 CFR 600.730(c)(3)and(4)) - All commercial fishing vessels with greater than a 4 foot of freeboard are requred to carry a boarding ladder. The ladder must be sufficient to allow authorized boarding officers and observers to board the vessel while at sea. This is a requirement of the Magnason Stevens Act related to fisheres enforcement.
- Federal Register dated 17 Nov 2008 - Which published the final rule related to the requirement for commercial fishing vessels with greater than a 4 foot freeboard to carry a boarding ladder. Effective date of this regulation is 1 Jan 2009.
- HQ Safety Flyer - Dated Jan 2009 this flyer released by Coast Guard Headquarters provides applifying information about boarding ladders..
- Boundary Line Determinations
- Boundary Line General Definition - 46 CFR 7.5(c)
- Boundary Lines Definition - Boundary Lines are defined in 46 CFR 7. In general, the Boundary Lines follow the trend of the seaward high water shorelines and cross entrances to small bays, inlets and rivers. Where the boundary line differs from the above definition the lines have been plotted on the below Google Maps.
- Deviations of Boundary Line in Northwest District. 46 CFR 7.140 & 7.145- There are 4 locations in the Northwest District where the boundary line deviates from the general definition.
- 13th District Boundary Line Message P170126Z FEB 94- Provides a simplified location for the boundary line for the Puget Sound applicable to enforcement. The boundary line is a line drawn north from Angeles Point. This is also a 13th District Ltr dated 14 July 92 with same definition.
- Canadian Albacore Tuna Vessels
- Canadian vessels are allowed to fish in US waters. The do not have to comply with US commercial fishing vessel safety regulations, but must comply with Canadian safety regulations. If major deficiencies are found they should be reported to District dre. District will contact Canadian authorities regarding the issue and negotiate a proper response. There are certain especially hazardous condtioins that do warrant termination and a highlighted in the OPORDER.
- Casualty Reporting
- Coast Guard Investigations site Link to Coast Guard Headquarters' Office of Investigations and Casualty Analysis (CG-INV) for casualty reports, reporting forms and policies.
- NVIC 01-15- Title 46, Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), Part 4 Marine Casualty Reporting Procedures Guide with Associated Standard Interpretations.
- 46 CFR 28.80 - This regulation requires the reporting of marine casualties to the Coast Guard and to the Marine Index Bureau. This information is to be used by the Coast Guard to identify casualty trends and work to reduce these casualties.
- 46 USC 6104 - This is the US Code that is the law behind 46 CFR 28.80.
- Federal Register Aug, 14 1991 - This is an excerpt from the Federal Register that announced the final rule of the Fishing Vessel Safety Act and has a discussion as to public comment on this specific regulation, and provides good historical information about the subject of 46 CFR 28.80.
- 46 CFR 28.90 - This regulation requires crew members to report within seven days injuries, illness or disability to the master/operator or agent of the employer of a commercial fishing vessel.
- 46 CFR 28.165 - This regulation requires the posting of the "Injury Placard".
- Charts: (See "Navigation" folder below)
- Citizenship - All Officers required by regulation are required to be US citizens 46 USC 8103(a). Every documented vessel is required to be under the command of a US citizen. 46 CFR 15.805(b).
- - 75/25 rule 46 USC 8103(i), applicable to all vessels:
- - at least 75% of unlicensed seaman (including fish processors) must be either:
- .......* A U.S. citizen or,
.......* An alien lawfully admitted to the United States for permanent residence
.......(Green Card)
.......- - up to 25% of unlicensed seaman (including fish processors) can be:
- ......* Any other alien allowed to be employed under the Immigration and Nationality
........Act (H-2B Work Visa)
.......
- Federal Register dated Feb 14, 2014 - Guidance for citizenship waiver. This guidance is hereby placed in the regulations in 46 CFR 28 SubPart I as posted here in the federal register.
- HQ Memo dated Mar 14, 2014 - Cancellation of MOC Policy Ltr 01-02.
- HQ Memorandum date June 8, 2005 - Guidance for citizenship requirements for crew aboard undocumented commercial fishing vessels.
- Class Rules
- Det Norske Veritas (DNV) Class Rules - Rules for Domestic Class U.S. Fishing Vessels.
- COLREGs Lines of Demarcation
- Demarcation Line Listing - This is a document that provides easy access to the various COLREGs Demarcation Lines. Links are listed by location around the country and provides access to the legal description as to it's location. Vessels that operate inside the lines of demarcation are required to carry a copy of the inland Navigation Rules.
- Construction requirements for new vessels
- 46 USC 4502(h) - Fishing vessels and Fish Tender vessels less than 50 feet overall in length built after July 1, 2010 that operates beyond 3 nautical miles from the territorial sea baseline or 3nm from the coastline in the Great Lakes.
- Shall be constructed in compliance with the recreational boating safety standards in 33 CFR Part 181 and 33 CFR Part 183 as applicable.
- 46 USC 4503(c)(1) - Fishing vessels and Fish Tender vessels 50 feet and greater and less than 79 feet overall in length built after July 1, 2013 to February 8, 2016 that operates beyond 3 nautical miles from the territorial sea baseline or 3nm from the coastline in the Great Lakes or that carries more than 16 individuals on board, or in the case of a fish tender vessel engaged in the Aleutian trade.
- Must be built and maintained to class rules by the ABS or similarly qualified organization accepted by the Coast Guard.
- 46 USC 4503(c)(2) - Fishing vessels and Fish Tender vessels 50 feet and greater and less than 180 feet overall in length built after February 8, 2016 that operates beyond 3 nautical miles from the territorial sea baseline or 3nm from the coastline in the Great Lakes or that carries more than 16 individuals on board, or in the case of a fish tender vessel engaged in the Aleutian trade must comply with 46 USC 4503(e) (below) or the alternative requirements established by the Coast Guard (TBD).
46 USC 4503(a) - Fishing vessels and Fish Tender vessels 79 feet and greater overall in length built after July 1, 2013.
- 46 USC 4503(e) - Must be designed by a state licensed naval architect or marine engineer.
- The design must incorporate standards equivalent to a classification society accepted by the Coast Guard or another qualified organization approved by the Coast Guard.
- Construction must be overseen and certified in accordance with its design by a Marine Surveyor accepted by the Coast Guard.
- The vessel must complete a stability test.
- - Have written stability and loading instructions.
- - Be assigned a loading mark.
- Must not be substantially altered without review and approval of a state licensed naval architect or marine engineer.
- Vessel must undergo a condition survey twice in a 5 year period not to exceed 3 years between surveys.
- Vessel must undergo an out of the water survey at least once every 5 years.
- Maintenance records to demonstrate compliance with the above and make available to the Coast Guard upon request.
- Must be built and maintained to class rules by the ABS or similarly qualified organization accepted by the Coast Guard.
- 46 USC 4503(b) - Fish Processing vessels built or that underwent or undergoes a major conversion after July 27, 1990,
- Must be built and maintained to class rules by the ABS or similarly qualified organization accepted by the Coast Guard.
- 46 USC 4503(d)(5) - A Fishing vessel, Fish Tender vessel or Fish Processing vessel that was classed before July 1, 2012.
- Must maintain class by the ABS or similarly qualified organization accepted by the Coast Guard, unless the service of the vessel will be inside 3nm from the territorial sea baseline and carry less than 16 individuals on board and in the case of a Fish Tender vessel will not engage in the Aleutian trade.
- CPR and First Aid Training
- CFIVS Final Rule Federal Register- Dated Aug 14, 1991 a valid CPR or first aid card is not required. The person needs only to provide proof that they have attended the training. See discussion in the final rule language.
- Dead Ship Tow
- Guidance for vessel being towed on a one-way voyage for purposes of scrapping or permanent removal from navigation. U.S. Customs and Border Protection requires that U.S vessels require clearance prior to being towed to a foreign port for permanant removal. Prior to being towed the local U.S. Coast Guard Officer In Charge Marine Inspection (OCMI) must be satisfied that certain conditions are met. Guidance is referenced in the Marine Safety Manual Vol II - Section B, Chapter 1 Paragraph B-8. Guidance for Coast Guard issuance of an International Loadline for a "one way" voyage is covered in the Marine Safety Manual Vol IV, Chapter 6.F.3.c(1). A table of issues that should be considered by the Coast Guard are provide here.
- Decals (Commercial Fishing Vessel Safety Decal)
- HQ Memorandum 02 March 2017 clarifies that the decal is issued to the vessels owner, anytime the Coast Guard is made, or becomes, aware of a change in ownership of a commercial fishing vessel, that vessel must be re-examined to ensure compliance with current requirements and regulations. You can also find a statement on the CG-5587 near the bottom of the first page, in the "Congratulations" block that states... "The Decal is to be removed from the vessel if the vessel is sold."
- Documentation (Vessel documentation and state registration)
- 46 CFR 67.7- Vessels required documentation. Fishing vessels of 5 net tons or greater are required to be documented..
- 46 CFR 67.21- Fisheries Endorsements for documented vessels. In order to engage in commercial fishing a documented vessel must have a fisheries endorsement. Only vessels built in the United States are eligible to obtain a fisheries endorsement. Vessel not constructed in the United States are not eligible. See the link for other vessels that may receive a fisheries endorsement.
- STATE REGISTERED VS DOCUMENTED TONNAGE GUIDANCE - How to determine if a state registered vessel should be required to be documented. This guidance only applies to US built hulls and vessels that have been state registered for years.
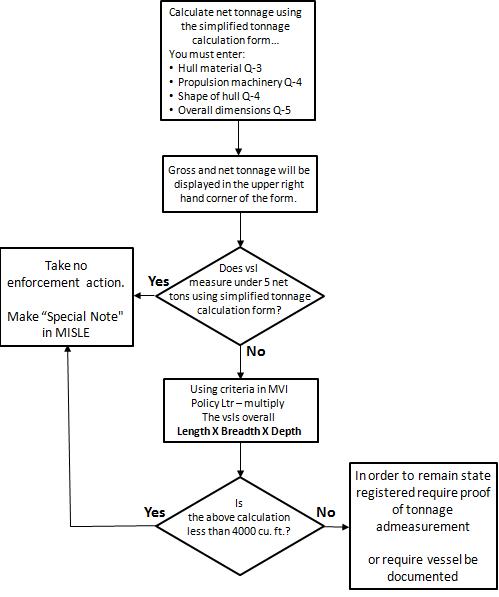
- 46 CFR 67.105 - Gross and net tonnage can be calculated using simplified tonnage calculations or by certificate of measurement.
- 46 CFR 67.95 - Evidence vessel was built in US.
- 46 CFR 69.203 - Definitions for overall length, overall breadth and overall depth.
- Documentation and Tonnage Brochure - This informational brochure provides an overview of federal documentation and tonnage measurement requirements for owners of U.S. commercial vessels less than 79 feet in overall length.
- MVI Policy letter - dated 26 Oct 1990, vessels greater than 5 net tons are required to be documented. This policy letter provides rule of thumb guidelines by using length, depth and breadth measurements in order to obtain a cubic foot measurement. Vessels that measure greater than 4000 cu ft are over 5 net tons and should be required to be documented unless admeasured by a naval architect and issued a tonnage certificate for less than 5 net tons.
- Simplified tonnage calculation form
- Drug Testing / Alcohol Testing
- Pre-employment Drug Testing 46 CFR 16.210 - Pre-employment testing is only required for commercial fishing vessels greater than 200 gross tons and only applies to licensed personnel required aboard the vessel.
- Periodic Drug Testing 46 CFR 16.220 - Periodic testing is only required for commercial fishing vessels greater than 200 gross tons and only applies to licensed personnel required aboard the vessel.
- Random Drug Testing 46 CFR 16.230 - Randon drug testing programs are only required for commercial fishing vessels greater than 200 gross tons and only applies to licensed personnel.
- Post Casualty Drug Testing after a Serious Marine Incident 46 CFR 4.06 - Each individual engaged or employed on board the vessel who is directly involved in the incident 46 CFR 4.03-4. That normally includes all crew working aboard the vessel. A Serious Marine Incident is defind in 46 CFR 4.03-2 . Federal Register Final Rule for this regulation is also available here.
- Alcohol testing 46 CFR 4.06-15(a)
-
Alcohol testing of all crew is required within 2 hours of a serious marine incident. All vessels must carry a sufficient number of alcohol testing devices aboard the vessel, The alcohol testing devices need not be carried on board if obtaining the devices and conducting the required alcohol test can be accomplished within 2 hours of a serious marine incident.Alcohol testing collection training 46 CFR 4.06-15(a) -Collection of an individuals saliva or breath must be taken only by personnel trained to operate the alcohol-testing device in use. There is no specific guidance on what that training should entail. 46 CFR 4.06-3(a)(2) states "Alcohol-testing devices must be used according to the procedures specified by the manufaturer of the testing device. In addition the marine employer shall ensure a CG-2692 and the supplemental form CG-2692b is submitted which includes the following as required by 46 CFR 4.06-12:
* Identity of those individuals tested positive
* Specify method used to obtain evidence
* Entry made in official log book (if carried)
* Individual(s) that refused the test.Drug Testing after a Serious Marine Incident 46 CFR 4.06-15(b) - in addition to the requirement to test for alcohol within 2 hours, testing for other drugs must be conducted on crew within 32 hours of a serious marine incident.
- Drill Conductor Training
- NVIC 7-93 - Dated Aug 24, 1993, this provides guidance for accepting course curriculum for the training of Drill Instructors who are then qualified to teach Drill Conductors how to conduct drills aboard commercial fishing vessels.
- NVIC 5-95 - Dated Jun 21, 1995, this provides approval requirements for organizations that offer Coast Guard approved courses.
- MSM Vol III Chapter 7 - Covers approval requirements for Coast Guard approved courses.
- Ebola
- MSIB 17-14 Ebola Virus Precautions (Change 1) - Dated Oct 22, 2014 - Ebola risks and the responsibility of vessel/facility agents, owners, masters, operators, Area Maritime Security Committee members, and persons to immediately report potential communicable disease hazards to the United States Coast Guard (USCG) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- EPIRBs
- Fatigue / Crew Endurance
- Fishing, Fatigue, and Crew Endurance Management Pamphlet - Provides recommendations for managing fatigue and reduce effects of fatigue.
- Crew Endurance Management Pamphlet- Recommendations for setting up a Crew enduarance Management program.
- FCC Ship Station License
- 47 CFR 80.13 - A ship station license is required for vessels that are required to carry a radio as per 46 CFR 28.245. If your vessel is required to carry a radio(s) you must have a valid ship station license displayed aboard your vessel for each required radio. Use this job aid to guide you using the FCCs website to apply for a ship station license.
- Fire Extinguishers
- Click here - This is the final rule issued July 22, 2016 - Harmonization of Standards for Fire Protection, Detection, and Extinguishing Equipment;
- Job Aid of new fire extinguishing requirements.
- Freeing Port Area Calculator
- Click here - Make sure to select "enable editing" then put in the current vessels dimensions in the space to the right of the arrows to get the minimum freeing port area. Once all 3 have been entered the minimum freeing port area will be displayed.
- Freezing Spray and Icing Reporting
- Click here - National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and Environment Canada request reporting of freezing spray conditions on your vessel.
- Garbage: (See "Pollution" folder below)
- GMDSS - Global Maritime Distress and Safety System
- 47 CFR SubPart W - The entire SubPart W for reference (parts 80.1065 to 80.1135)
Sea areas 47 CFR 80.1069 ...
A-1 out to approximately 20 to 30nm from shore. Within range of VHF coast station where DSC (direct selective calling) is continuously available.
A-2 out to about 100nm from shore. Within range of MF coastal stations where DSC is continuously available.
A-3 beyond areas A-1 and A-2, but within satellite coverage areas roughly between 70 degress north and 70 degrees south latitudes.
A-4 remaining sea areas (polar regions).- 47 CFR 80.1065 thru 80.1135 - Applies to all fishing vessels 300 gross tons and greater. Vessel operating in sea areas A-1 and A-2 are currently exempt provided:
- (1) The ship is equipped with:
... (i) A VHF radiotelephone installation.
... (ii) A MF or HF radiotelephone installation.
... (iii) A Category 1, 406.0–406.1 MHz EPIRB meeting the requirements of
...... §80.1061;
... (iv) A NAVTEX receiver meeting the requirements of §80.1101(c)(1);
... (v) Survival craft equipment meeting the requirements of § 80.1095;
... (vi) A Search and Rescue Transponder meeting the requirements of
........§80.1101(c)(6); and
(2) The ship remains within coverage of a VHF coast station and maintains a continuous watch on VHF Channel 16; or
(3) The vessel remains within coverage of an MF coast station and maintains a continuous watch on 2182 kHz and VHF Channel 16.- NVIC 3-99 - GMDSS Requirements - Provides guidance for what GMDSS equipment is required for vessels.
- 47 CFR SubPart W -RADIO OPERATORS - 2 licensed operators with GMDSS endorsement required for vessel 300 gross tons and greater (47 CFR 80.1065(a)), and beyond 100 miles from shore (Beyond sea areas A-1 and A-2). (The greater than 100 miles from shore comes from 47 CFR 80.1071 (Exemptions) paragraphs (c)(2) which exempts vsls that can remain within VHF coverage areas and (c)(3) which exempts vsls that can reamain withing MF coverage areas). 47 CFR 80.1073 discusses the radio operator specific requirement. NOTE this does not align with NVIC 3-99. According to Russ Levin with GMDSS committee HQ the NVIC needs to be updated to align with the regulations but has not been updated. Follow CFR requirements.
- FCC Exemption Order effective Feb 1, 1999
- Termination of 2Mhz watchkeeping - This is a Safety Alert issued 23 Jun 2013 by the Coast Guard providing notification that the Coast Guard will no longer be monitoring medium frequency (2-4mHz) emergency and weather alert frequencies.
- HQ Memo GMDSS Requirements for CFVs Operating in Alaska Waters - Dated 1 August 2014. The Coast Guard will not be announcing the opening of Sea Areas A-1 or A-2 for waters off of Alaska. This memo clears up questions about GMDSS equipment carriage requirements for commercial fishing vessels operating in Alaska waters.
- GMDSS Task Force Information Bulletin on Tonnage Interpretations - This document last updated 6 January 2007, discusses whether Regulatory or Convention (ITC) tonnage can be used for applicability of GMDSS. Regulatory tonnage can be used for US Flag vessels on domestic voyages.
- Hawaii Class Exemption (suvival craft & EPIRBs)
- MSIB D14-01-15- This Marine Safety Information Bulletin is applicable to vessels operating in the waters off of Hawaii. It provides a class exemption to any commercial fishing vessel less than 36', operating within 15nm from shore, with four or less people onboard from the survival craft and emergency position indicating radio beacon (EPIRB) requirements.
- Hull Repairs / Inspection
- NVIC 7-68 - Notes on Inspection and Repair of Steel Hulls
- NVIC 8-87 - Notes on Design, Construction, Inspection and Repair of Fiber Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Vessels
- NVIC 7-95 - Guidance on Inspection, Repair and Maintenance of Wooden Hulls
- NVIC 7-01 - Procedures for Hull Inspection and Repair on Vessel Built of Riveted Construction
- Non-destructive Testing of Wood Hulls - A report from the Coast Guard Research and Development Center - This paper reports the results of a project at the Coast Guard R&D Center which has tested and identified some methods which may be utilized to improve the inspection of wooden vessels. In this project, previous work performed for inspection of wooden structures was reviewed and those which held the most promise were evaluated on a donated vessel.
- Law Enforcement Guidance
- ALDIST 162/99 - provided guidance for law enforcement personnel .
Vessel with decals should be spot checked for the "Big 8" -
- PFDs,
survival craft,
EPIRBs,
fire extinguishers,
visual distress signals,
high water alarms,
drills and training,
watertight integrity and
stability- Licensing
- Masters - every self propelled, seagoing documented vessel of 200 GT or greater is required to have a licenced master 46 USC 8304 and 46 CFR 15.805(a)(1).
- Mates -any person in charge of navigating the vessel or standing a navigation watch on a self propelled, seagoing documented vessel of 200 GT or greater is required to be appropriately licensed. 46 CFR 15.810(c). A person that stands a lookout watch as required by Rule 5 of the Nav Rules is required to be a member of the navigation watch 46 CFR 28.850.
- Chief Engineers -a person that has operation or maintenance responsibilites for the propulsion machinery aboard a seagoing documented vessel of 200 GT and greater is required to hold an appropriate license 46 CFR 15.820(b).
- Asst Engineers - a person in charge of an engineering watch aboard a mechnically propelled seagoing documented vessel of 200 GT or greater is required to hold an appropriate license 46 CFR 15.825(a). It is the responsiblity of the vessel master to establish the watch 46 CFR 15.705(a).
- HQ Policy Ltr 11-11 - Engineering Officer Endorsements on Uninspected Fishing Vessels - dated 7 Oct 2011. Provides criteria for each level of engineering officer. Requires compliance by Jan 1, 2014.
- HQ Msg R 061640Z DEC 13 - Extension of date for compliance with Policy Ltr 11-11 - extends compliance to 1 Jan 2014.
- 46 CFR 15.103(e) - STCW requirements for fishing vessels - Licenses are only required for vessels greater than 200 GT. STCW is only required for licensed mariners of fish processing vessels that do not fish (including Mothership operations). Licensed mariners of fishing vessels as defined in 46 USC 2101(11)(a) and fish tender vessels as defined in 2101(11)(c) are not required to have STCW endorsements.
- Federal Register Dated March 20, 2015 - Change 1 to HQ policy letter - official release of the policy letter see below.
- HQ Policy Ltr 11-11 Change 1 - Extension of date for compliance with Policy Ltr 11-11 - extends compliance to Oct 15, 2015. Provides for additional time on case by case basis as agreed to by the cognizant OCMI..
- Load line Guidance
- Loadline Job Aid - this is a flowchart (not official document) that assists in determining whether a vessel is required to have a loadline or not based on 46 USC 5102. This job aid also references vessel on a foreign voyage. According to 46CFR42.03-5 "all US vessels which engage in a foreign voyage or international voyage by sea are subject to the loadline regs". 46CFR42.05-45 an international voyage "means a sea voyage from any country to any port outside that country , or conversely". Note this does not include Canada when navigating on sheltered waters of Puget Sound and contiguous west coast waters of United States and Canada see 46CFR42.03-35.
- MVI Policy Ltr 14-90- dated Jun 20, 1990 this discusses fish processors, the requirement for them to be loadlined and discusses what types of processes qualify as processing or not.
- Major Conversion
- 46 U.S.C. § 2101(14a) - US Code definition of Major Conversion.
- Policy Decision HQ 7 Jan 1997 - Letter of response to David Green on a policy decision that a change of the type of vessel from Fishing / Tender / Processor is major conversion.
- HQ guidance document - released in 2012 - For the purposes of meeting requirements of an alternate safety compliance program, the term “substantial change,” has the same meaning as the term “major conversion” as defined by 46 U.S.C. § 2101(14a). A substantial change or major conversion under this definition means a conversion of a vessel that: substantially changes the dimensions (e.g. length, breadth, or depth) or carrying capacity of the vessel; changes the type of the vessel; substantially prolongs the life of the vessel; or, otherwise so changes the vessel that it is essentially a new vessel, as decided by the Commandant.
- Manning Guidance
- Manning Job Aid - this is not an official document but a job aid to help determine manning requirments for specific fishing industry vessels and includes references to the regs.
- MSM Vol III, Chapter 26, par 3. - provides general guidance for manning levels of certain commercial fishing industry vessels.
- Masters - every self propelled, seagoing documented vessel of 200 GT or greater is required to have a licenced master 46 USC 8304 and 46 CFR 15.805(a)(1).
- Mates -any person in charge of navigating the vessel or standing a navigation watch on a self propelled, seagoing documented vessel of 200 GT or greater is required to be appropriately licensed. 46 CFR 15.810(c). A person that stands a lookout watch as required by Rule 5 of the Nav Rules is required to be a member of the navigation watch 46 CFR 28.850.
- Chief Engineers -a person that has operation or maintenance responsibilites for the propulsion machinery aboard a seagoing documented vessel of 200 GT and greater is required to hold an appropriate license 46 CFR 15.820(b).
- Asst Engineers - a person in charge of an engineering watch aboard a mechnically propelled seagoing documented vessel of 200 GT or greater is required to hold an appropriate license 46 CFR 15.825(a). It is the responsiblity of the vessel master to establish the watch 46 CFR 15.705(a).
- Watches - Establishment of adequate watches is the responsibility of the master 46 CFR 15.705(a). Also see the discussion in the MSM Vol III.
- See also "Licensing" (above)
- Marine Pollution - MARPOL: (See Pollution folder below)
- Marine Sanitation Device (MSD)
- 33 CFR 159.7(b) - Securing of Type I and Type II s MSDs - These type devices treat the sewege in preparation for pumping overboard and required to be certified to meet Coast Guard standards. This treated waste may be discharged in waters including inside 3 miles from shore (except those locations designated as NO DISCHARGE ZONES see link below)
- 33 CFR 159.7(c) - Securing of Type III s MSDs - A Type III device is a simple holding tank. Since the affluent is not treated, pumping overboard is more restricted. Untreated sewage can not be discharged inside 3 miles from shore. There may be additional restrictions for each state.
- 40 CFR 140.3(b)(2) - Areas where discharge is allowed
- No discharge zone website
- 40 CFR 140.4 - States rights to prohibit discharge
- Navigable Waters of the Northwest District
- Navigable Waters List - Excerpt from the Northwest District SOP.
- Navigable Waters Legal Determination "Rufus Lake" - Legal determination of request as to navigable waterway status of Rufus Lake on the Columbia River between Chief Joseph and Grand Coulee Dams. This area determined to be navigable and therefore subject to Coast Guard jurisdiction.
- Navigation
- Navigation Rules - COMDTINST M16672.2D - The entire pamplet of the Navigation Rules. NOTE that the Inland Nav Rules are required for vessels anytime the vessel operates inside the COLREGs Demarcation Lines. This job aid provides a listing of lines of demarcation around the country. If a vessel never crosses inland of the these lines, the vessel is not required to carry a copy of the inland nav rules. There is no requirement for commercial fishing vessels to carry a copy of the International Navigation Rules.
- Navigation Lights - COMDTINST M16672.2D - Excerpts and pics from rule 3 which defines "vessel" and "vessel engaged in fishing", and rule 21 nav light configurations based on vessel length and type fishery engaged.
Navigation light configurations for various types of fishing operations are based on size and vessel fishing apparatus which may restrict vessel maneuverability.
Restricted in ability to maneuver are fishing oerations such as whenworking fishing gear such as long line gear or during the time the vessel is hauling in a seine net.
Not restricted are fisheries such as a troller that can move out of the way of another vessel while continuing to fish.
Less than 7 meters (23')
- Trawler
- Restricted (when working fishing gear)
- Not restricted (trollers)
Less than 12 meters (39.4')
- Trawler
- Restricted (when working fishing gear)
- Not restricted (trollers)
Less than 20 meters (65.6')
- Trawler
- Restricted (when working fishing gear)
- Not restricted (trollers)
Less than 50 meters (164.1')
- Trawler
- Restricted (when working fishing gear)
- Not restricted (trollers)
50 meters (164.1') or greater
- Trawler
- Restricted (when working fishing gear)
- Not restricted (trollers)
- Operating without a Lookout (Rule 5) of the Nav Rules - Nav Rule 5 - Maintaining a proper lookout - Although a common practice, it is a violation of the navigation rules to drift at night while all crew sleeps.
NOTE: A vessel at anchor is not relieved from the requirement to maintain a lookout. There are various references to this specific example, visit http://navruleshandbook.com/Rule5.html under "Prevailing Circumstances and Conditions".- Use of Electronic Navigation Pubs / Charts in Lieu of paper. - NVIC 01-16 Change 3 - allows the use of electronic versions of Navigation Pubs to include Light List, Local Notice to Mariners, Tide and Current Tables, Coast Pilot, VTS Rules. This circular describes equivalencies for electronic charts, electronic publications, and ENC-derived paper charts in lieu of the carriage requirements found in 33 CFR and 46 CFR and to provide procedures for conducting inspections for vessels electing to comply with one or more of the equivalencies.
- NOAA/NMFS MOAs
- Memorandum of Agreement on Observer Safety - National agreement signed December 21, 2004, this memo estblishes information sharing from NMFS Observer reports and institution of overall cooperation to improve Observer safety.
- Memorandum of Agreement on NMFS Charter Agreements - This agreement was signed June 4, 2021. The Coast Guard will examine the vessel contracted to work a specific charter agreement and issue a Letter of Examination (see Appendix A of the Charter Agreement) for the length of the charter agreement. During the exam attention will be payed to ensure there is sufficient survival craft capacity for all crew and NMFS workers, there is sufficient personal floatation devices / Immersion Suits for all on board and check that a station bill includes the additional NMFS personel, also discuss with the Master of the vessel that all NMFS workers are involved in the safety orientation and emergency drills.
- Notice of Violations
- Notice of Violations User's Guide - The guide provides the procedures and a list of prorposed penalty amounts.
- Oceanographic Research Charter of Commercial F/V
- On occasion national or state fisheries agencies charter a commercial fishing vessel to do oceanographic or limnological research. These vessel are not required to be inspected as Oceanographic Research Vessels in accordance with 46 CFR Subchapter U because they are not "being employed only in oceanographic instruction or research". These charters are considered as uninspected passenger vessels. If the vessel has a valid dockside examination decal and properly licensed crew including a master with at least a uninspected passenger vessel license or better this vessel can operate. The cognizant OCMI should be notified. The NMFS and the USCG have an (MOU) that establishes an inspection requirement when they charter a vessel.
- NMFS / USCG MOA (May 1980) -the NMFS desired an increased level of safety for their charters prior to the implementation of the CFIVS regs and entered into this MOA with the Coast Guard. This is an old MOA that was established prior to the implementation of the CFIVS act and references requirements in 46 CFR Subchapter "C" and some parts of Subchapter "T". Although still valid HQ is working on a new MOU that will adopt 46 CFR Part 28 as the acceptable criteria.
- Marine Safety Manual Vol II, B-4-H) -This guidance updates the MOA. Since the MOA was signed in 1980, the Congress passed the Commercial Fishing Vessel Safety Act in 1988 that went into affect in 1991. So references to Subchapter T are not appropriate as fishing vessels have mandatory safety requirements now. 28 as the acceptable criteria.
- OSHA - Occupational Safety and Health Administration
- OSHA Policy Guidance - This instruction includes MOAs (Memorand of Agreement) and consolidates a lot of dispersed information. Includes information regarding OSHA Jurisdiction from the Observer program regarding, safe boarding of the vessel at the plant lighting, gangway, pfds… and also OSHA jurisdiction within the vessels processing plant.
- Paper Captain - Non United States Citizen in charge of a United States documented vessel
- 46 USC 12131 - A United States documented vessel may be placed under the command only of a citizen of the United States.
- Passengers for hire on Commercial Fishing Vessels
- D17 District Instruction -Dated april 10, 2013, this instruction outlines the requirements for commercial fishing vessels that carry passengers for hire. D17 businesses have seen an upstart of an industry of people that want to experience what it is like to work on a commercial fishing vessel as many have seen on television.
- Personal Marker Light batteries replacement (scheduled maintenance Table 28.140)
- NVIC 1-92 (Enclosure 5) - Regular batteries sold over the counter such as 9 volt and A, C or D cells even though they have a date must be replaced annually. Special marine type battereis marked with an expiration date must be replaced after the date marked on the battery.
- Pollution
- Anti Fouling Paint Policy - CG-CVC Policy Ltr 12-08 dated Oct 15, 2012
- Anti Fouling Paint - IMO Resolution
- Emissions - MARPOL VI - Enforcement of Emission Controls - CG-CVC Policy Ltr 12-04 dated July 25, 2012. Guidance for enforement.
- Emissions - MARPOL VI - Job aid - HQ CG-CVC job aid released 07/24/2012 to be used by Coast Guard Marine Inspectors to inspect and document deficiencies duing inspactions and reexaminations.
- Garbage Placard 33 CFR 151.59 - Vessels > 26'
- Garbage - Federal Register - latest change to 33 CFR 151 MARPOL V - Garbage discharge - this is the latest change to the regulations released in the Federal Register dated February 28,.2013.
- Garbage - HQ Policy Ltr 13-01 Interim guidance for revised MARPOL Annex V Implementation - dated Feb 26, 2013 provides interim guidance for implementation to the changes of MARPOL V garbage discharge regulations. Until regulations are promulgated and placards are available US flagged fishing vessels may continue to use existing placards.
- Garbage Log 33 CFR 151.55 - Ocean going vessel > 400GT.
- IOPP Certificate CG-5352 - issued to commercial fishing vessels greater than 400GT on a foreign voyage. This is a requirement of the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships, 1973, as modified by the Protocol of 1978 (MARPOL 73/78). The IOPP certificate is a requirement of MARPOL Annex I - Prevention of pollution from oil for ships. An examination of the vessel is conducted in accordance with 33 CFR 151.23 and form CG5352A. Once found in compliance a commercial fishing vessel is issued form CG-5352 IOPP certificate which is valid for 5 years with a requirement for annual endorsements. A commercial fishing vessel is also issued the CG-5352A which is a supplement to the IOPP Certificate.
- IOPP Certificate CG-5352A - supplement (form A) to the CG5352.
- Oil Pollution Placard - 33 CFR 155.450 - Vessel > 26'
- Shore Connection - MOC Policy Ltr 2-97 - HQ determined that 1.5 inch quick disconnects is an acceptable equivalent to the standard shore connection normally required. This does not apply to oceangoing vessels 400 GT or greater on international service.
- Waste Management Plan 33 CFR 151.57 -Ocean going vessel > 40'
- Radios: (See "Transmitting Equipment" folder below)
- Registration: (See "Documentation" folder above)
- SOLAS
- Chapter I, Part A -"Applications, definitions, etc" Regulation 3 - "Exceptions" paragraph (a) - SOLAS requirements are not applicable to fishing vessels. It is applicable to fish tender and fish processing vessels that go on a foreign voyage.
- Stability Guidance
- MSC Stability Guidance Document - Guidance dated Mar 21, 2013 from the Marine Safety Center on submitting stability calculations to the MSC. The MSC reviews CFV stability for load line assignment at the request of an Officer in Charge, Marine Inspection (OCMI), for a vessel of concern, or as part of their oversight of an Authorized Classification Society. The guidance in this document applies to both new and existing vessels.
- State Numbering of Vessels
- - vessels measuring under 5 net tons can be registered with the state in which the vessel owner resides according to that states law in lieu of being documented.
- 33 CFR 173.27
- Simplified tonnage measurment calculation form
- STCW - (Standards for Training, Certification and Watchkeeping)
- 46 CFR 15.103(e) - STCW requirements for fishing vessels - . STCW is not required for licensed mariners of fishing vessels. Mariners licenses are only required for vessels greater than 200 gross tons.
STCW is required for licensed mariners of fish processing vessels that do not catch fish (including Mothership operations). Licensed mariners of fish processors that do catch fish are exempted from STCW.
STCW Convention Article II paragraph (f) defines only a fishing vessel, in Article III paragraph (b) states fishing vessels are exempt from STCW. There are no other fishing vessel definitions. So if a fish processing vessel also fishes the licensed mariners for those vessels are exempt from STCW.
46 CFR 15.103(e) also states that fishing vessels used as fish-tender vessels are also exempt from STCW. Definitions for fishing vessel is in 46 USC 2101(11)(a) and fish tender vessel is defined in 46 USC 2101(11)(c).
- Survival Equipment
- FAQs about the servicing of Survival Craft - Dated Sept 1999 this letter from HQ Life Saving Standards Division, included information about why annual servcing of inflatable survival craft is required. This is a good reference.
- Painter line for buoyant apparatus and life floats NVIC 01-83
- Retroreflective Material Installation NVIC 01-87
- Implementation of Life Saving Equipment Requirements - NVIC 1-92 - dated 4 Feb 1992, initial guidance which replaced NVIC 5-86 (voluntary CFIVS regs) related to lifesaving equipment.
- Change 1 to NVIC 1-92 - dated 2 Aug 1992, this NVIC clarifies regulations and policies concerning inflatable life rafts. Use of non-SOLAS approved for applications where 4 person life raft is allowed.
- Change 2 to NVIC 1-92- dated 4 Mar 1994, this NVIC temporarily revised the allowed carrying capacity of certain unapproved inflatable liferafts for commecial fishing vessels. This expired January 1, 1999. THIS IS PROVIDED AS HISTORICAL INFORMATION.
- Excess Equipment MOC Policy Ltr 01-96 - Excess survival equipment aboard commercial fishing vessels. Excess survival equipment can be kept on board if used for drill purposes and must be marked "for training only".
- Unserviceable Survival Equipment - MOC Policy Ltr 04-08 - dated 6 August 2004 provides guidance on what should be done with unserviceable survival equipment on board commercial fishing vessels. Also discusses termination guidance for survival craft 5 months beyond service date, hydrostatic releases and disposable hydrostatic release units 5 months past expiration.
- An inflatable survival craft that is beyond its servicing date by 5 months must be removed from the vessel and serviced. Inflatable survival craft may not be kept on board and marked for drill use only, even if it is not required due to the vessels route.
- SOLAS - Excerpt from SOLAS that states international inflatable survival craft annual servicing requirement and 5 month max extenstion.
- Testing of Immersion Suits - NVIC 01-08 - dated 28 Jan 2008 provides recommended testing intervals for leak testing seams and closures.
- Note that this is not a legal requirement nor is it a rule. If during an inspection the condition of the immersion suit is in question due to the materail condition of the suit, the owner may elect to test the suit in order to prove its condition as being satisfactory.
- NMFS Observer Valise Liferafts Memo - dated 15 Jul 2008 allows the carriage of additional life raft aboard a commercial fishing vessel that is required to carry and National Marine Fisheries Servcie Observer if the vessel existing life raft has insufficient capacity for the added NMFS observer. This life raft is not SOLAS approved but my be used aboard a vessel operating in an area that is required to carry SOLAS life refts.
- Allowing the carriage of excess life saving equipment to prevent fatal falls overboard - interpretation. - In an affort to increase PFD use while working aboard commercial fishing vessels, Northwest District researched the issue of allowing the carriage of excess life saving equipment, specifically PFDs aboard commercial fishing vessels. This is a handout that spells out why this is allowed. This is an opinion paper released by the Northwest Coast Guard District.
- HQ Policy Letter 15-05 - Replacements for out of the water survival craft and replacement of life floats and rigid buoyant apparatus- Dated December 15, 2015 - As of February 26, 2016 vessels that were required to carry a life float or a rigid buoyant apparatus must be replaced with suvival craft that does not allow any part of a persons body to be immersed in water. This would require at least an inflatable buoyant apparatus or any inflatable life raft..
- Termination of Vessels Voyage
- Termination Authority - 46 CFR 28.65 - Dated Sept 1999 this letter from
- Termination of Unsafe Operations Aboard Commercial Fishing Industry Vessels NVIC 12-91 - This was initial guidance from HQ on termination for commercial fishing vessels. This has some good verbiage on the general stance on when terminations might be appropriate.
- Unserviceable Survival Equipment - MOC Policy Ltr 04-08 - dated 6 August 2004 discusses termination guidance for survival craft 5 months beyond service date, hydrostatic releases and disposable hydrostatic release units 5 months past expiration.
- Tribal vessel termination policy - 25 CFR 249.7 - Bureau of Indian Affairs
- Tonnage
- Tonnage Measurement Guidelines for Small Fishing Vessels - Dated 26 Oct 1990, this HQ Policy Letter discusses tonnnage measurement for small fishing vessels that could be considered under 5 net tons and thus allowed to be state registered as opposed to documentation with the Coast Guard. Provides simplified measurment to calculate volume less than 4000 cubic foot.
- Documentation and Tonnage Brochure - This informational brochure provides an overview of federal documentation and tonnage measurement requirements for owners of U.S. commercial vessels less than 79 feet in overall length.
- 46 CFR 69.203 - Definitions for overall length, overall breadth and overall depth.
- Simplified tonnage calculation form - You must fill in at least items 3 thru 6. Once these fields are complete the vessels Gross and Net Tonnage will appear at the top left side of the form.
- Training
- NVIC 7-93 - Dated Aug 24, 1993, this provides guidance for accepting course curriculum for the training of Drill Instructors who are then qualified to teach Drill Conductors how to conduct drills aboard commercial fishing vessels.
- NVIC 5-95 - Dated Jun 21, 1995, this provides approval requirements for organizations that offer Coast Guard approved courses.
- MSM Vol III Chapter 7 - Covers approval requirements for Coast Guard approved courses.
- HQ Policy Memo dated 22 April 2013 - Guidance on Providing Assistance to Commercial Training Organizations Offering Safety Training to Fishermen..
- Transmitting Equipment
- GMDSS Requirements - NVIC 3-99 - Provides guidance for what GMDSS equipment is required for vessels.
- Posting of FCC Station License - 47 CFR 80.405
- Requirement to carry FCC Ship Station License - 47 CFR 80.13 - An FCC SSL is not required for any radio communicating equipment that is not required by regulation. Only a commercial fishing vessel required to carry a radio as listed in 46 CFR 28.245 is required to have the license.
- Termination of 2 mHz distress watchkeeping
- Marine Safety Alert 06-13
- Telecommunications Policy - 2182 kHZ distress watchkeeping message - ALCOAST R142027Z 13 - Due to termination of watchkeeping on the 2 mHz band the Coast Guard will continue to monitor the following distress frequencies in the 4/6/8/12 mHZ bands for voice distress calls.
- ..............
- The Coast Guard will continue to monitor VHF channel 16 (156.8 mHz) and DSC channel 70 (156.525 mHz).
- Federal Register 15 Jul 13 - July 13, 2013 provides reasoning for termination of watchkeeping for the 2 mHz distress frequencies.
- Requirement to upgrade VHF Radios to DSC by Jan 20, 2016 vessels 300GT and greater- View Public Notice The FCC released a public notice dated April 16, 2015. This notice requires all commercial fishing vessels that are required to carry a VHF radio to replace them with VHF radios with Direct Selective Calling (DSC) capability by January 20th 2016.
- DSC VHF radios installed on vessel not required to carry them.- View Public Notice - The FCC released a public notice dated December 10, 2012. This notice states that if a non-compulsory ship installs a DSC radio, they must get an MMSI but they do not have to have GPS installed.
- Tribal Enforcement
- 25 CFR 249.7 - Bureau of Indian Affairs - Indian Tribes have special fishing rights, these regs specify that tribal vessels are not exempt from any law or regulation pertaining to safety, obstruction of navigable waters, national defense, security of public property, pollution, health, sanitation or registration.
- Work Vests
- 46 CFR 26.30 - Althouth work vests are not required to be carried aboard commercial fishing vessels, we highly encourage their use. This is to clarify that when these devices are carried aboard the vessel they MUST be maintained in serviceable condition. (Coast Guard Marine Safety Personnel should ensure the device is in serviceable condition in accordance wth the Coast Guard approval and if not, the work vest must be removed from the vessel and either repaired or destroyed. Highly encourage their replacement.)
- Bar Crossing and Navigation Guidance for Mariners (Oregon/Washington states)
- Thirteenth District Special Local Notice to Mariners 27 MAY 2020 - This Special Local Notice to Mariners is an annual publication containing important information for the mariners. Northwest District waterways include the seacoast from the California/Oregon border to the United States/Canadian border, and all waters subject to the jurisdiction of the United States in Idaho, Montana, Oregon and Washington.
- Federal Register Final Rule Nov 17, 2009 - The Captain of the Port (COTP) has the authority to either totally close the bar, or restrict the bar.
- Bar Closure - Done when the environmental conditions exceed the operational limitations of the relevant Coast Guard search and rescue resources as determined by the COTP. No vessels can cross the bar unless specifically exempted by the COTP.
Bar Restriction - When determined by the COTP, the bar is restricted to vessels as follows.
• Recreational vessels Cannot operate
• Uninspected passenger vessels Cannot operate
• Uninspected commercial F/V Must wear or have PFDs readily available- Federal Register Apr 12, 2010 - Change to the Umpqua River bar area.
- Chetco River
- Columbia River
- Coos Bay
- Couquille River
- Depoe Bay
- Grays Harbor
- Quillayute River
- Rogue River
- Siuslaw River
- Tillamook Bay
- Umpqua River
- Yaquina Bay
- Books / Manuals / Pamphlets
- Northwest District CFIVS Reference Guide - This is the .pdf version of the job aid, updated June 2024, this guide was developed by the Northwest District which encompasses the states of Washington, Oregon, Idaho and Montana. .
- Arctic District CFIVS Reference Guide - Last updated Aug 2016. This guide is specific to the applicability of the Commercial Fishing Vessel Safety Regulations for this district. .
- Pamphlet - Federal Requirements for Commercial Fishing Industry Vessels. - Updated through June 1, 2020, this is a pamphlet printed by the Commercial Fishing Industry Vessel Safety Program that provides information on each of the regulations applicable to commercial industry fishing vessels.
- Pamphlet - Deck Safety for Crab Fishermen. - dated 2002, this is a pamphlet published by Jensen Maritime Consultants to share practical ways to reduce deck injuries and falls overboard on commercial crab fishing vessels. *Posted with permission from Crowley Engineering Services, Sep. 2025
- Commercial Fishing Industry Vessels Best Practices Guide (updated December 2024). This guide was developed in collaboration with owners of fishing vessels, safety organizations, the Coast Guard and the National Commercial Fishing Safety Advisory Committee (NCFSAC). It provides safety recommendations to address identified risks within the fishing industry based upon careful analysis of vessel casualties and personnel fatalities and inuries.
- Commandant Instructions
- Commandant Instruction 16711.13B - (August 17, 1995) Implementation of the Commercial Fishing Industry Vessel Regulations..
- Commandant Instruction 16711.14 - (March 3, 1993) Commercial Fishing Industry Vessel Safety Training and Qualification .
- Definitions - If you do not find a definition but would like to have it added to this list please let me know at Michael.G.Rudolph@uscg.mil
- Boundary Lines Definition
Boundary Lines are defined in 46 CFR 7. In general, they follow the trend of the seaward high water shorelines and cross entrances to small bays, inlets and rivers. Where the boundary line differs from the above definition have been plotted on the below Google Maps.- Built
HQ guidance document - "Built" as used to delineate a vessels build date, is used throughout International Conventions, U.S. law, and Coast Guard regulations as the date when the vessels keel is laid or reaches a similar stage of construction. Consistent with those intentions, the term built, as it applies to newly constructed CFVs (post July 1, 2012, or post January 1, 2010 for smaller vessels, which are the effective dates in the CGAA), means: when a vessel’s keel is laid; or when construction identifiable with the vessel has begun.
- Coastal Waters
33 CFR 175.105 - Coastal waters include the waters from 3nm off shore to the first point where the waterway narrows to within 2nm across. Measurment should be made from points on the land when measured from the high water mark on the shoreline. On charts, blue tinted areas are always wet, green tinted areas are intertidal and are not land, buff color areas are land and are always dry.
- Coastwise
Coastwise is referenced under Personal Floatation Device Lights 46 CFR 25.25-13(a). There is no definition of coastwise in Part 28. The only definition for coastwise can be found in each inspected vessel subchapter related to a vessel routes.Although each of the above are applicable to its own subchapter we have adopted the general definition. "Coastwise" and is interpreted to mean coastal waters - 33 CFR 175.105 and waters out to 20 nautical miles off shore. (coastal waters include the waters from 3nm off shore to the first point where the waterway narrows to within 2nm across.Subchapter D - 46 CFR 30.10-11,
Subchapter H - 46 CFR 70.10-1,
Subchapter I - 46 CFR 90.10-11,
Subchapter K - 46 CFR 114.400,
Subchapter T - 46 CFR 175.400
Subchapter W - 46 CFR 199.30.- Fish
Defined in 46 USC 2101(11) - means finfish, mollusks, crustaceans, and all other forms of marine animal and plant life, except marine mammals and birds.- Fishing Vessel
Defined in 46 USC 2101(11a) - means a vessel that commercially engages in the catching, taking, or harvesting of fish or an activity that can reasonably be expected to result in the catching, taking, or harvesting of fish.- Fishing Processing Vessel
Defined in 46 USC 2101(11b) - means a vessel that commercially prepares fish or fish products other than by gutting, decapitating, gilling, skinning, shucking, icing, freezing, or brine chilling.- Fishing Tender Vessel
Defined in 46 USC 2101(11c) - means a vessel that commercially supplies, stores, refrigerates, or transports fish, fish products, or materials directly related to fishing or the preparation of fish to or from a fishing, fish processing, or fish tender vessel or a fish processing facility.- Foreign Voyage
Defined in 46 USC 3201(3) - A voyage from a place in the United States to a place in a Foreign Country.- High Seas
Defined in 46 CFR 25.26-1 - High seas means the waters beyond a line three nautical miles seaward of the Territorial Sea Baseline as defined in 33 CFR 2.20.- International Voyage
As it relates to Loadlines. 46CFR42.05-45 an international voyage "means a sea voyage from any country to any port outside that country , or conversely". Note this does not include Canada when navigating on sheltered waters of Puget Sound and contiguous west coast waters of United States and Canada see 46CFR42.03-35.- Length Overall or Overall in Length
Defined in 46 USC 2101(20b) - The horizontal distance of the hull between the foremost part of the stem and the aftermost part of the stern, excluding fittings and attachments. This definition is the one used in the language of the Coast Guard Authorization act used to determine a vessels length for applicabilty for being required to be classed and/or loadlined. It is also the determining factor for vessel required to comply with Alternate Safety Compliance programs to be developed.- Lines of Demarcation (COLREGs)
- This job aid provides a listing of lines of demarcation around the country. If a vessel never crosses inland of the these lines, the vessel is not required to carry a copy of the inland nav rules. There is no requirement for commercial fishing vessels to carry a copy of the International Navigation Rules.- Navigable Waters of the United States
Defined in 33 CFR 2.36 - means the Territorial Seas of the United States defined in 33 CFR 2.22. (See Territorial Seas definition below).- Oceans
Defined in 46 CFR 24.10 - Oceans means those waters beyond 20 nautical miles from shore.- Overall Length
Defined in 46 CFR 69.9 - Horizontal distance between the foremost part of a vessels stem to the aftermost part of the vessels stern, excluding fittings and attachments.- Substantial change
HQ guidance document - For the purposes of meeting requirements of an alternate safety compliance program, the term “substantial change”, has the same meaning as the term “major conversion” as defined by 46 USC 2101(14a). A substantial change or major conversion under this definition means a conversion of a vessel that: substantially changes the dimensions (e.g. length, breadth, or depth) or carrying capacity of the vessel; changes the type of the vessel; substantially prolongs the life of the vessel; or, otherwise so changes the vessel that it is essentially a new vessel, as decided by the Commandant.- Territorial Seas
Defined in 33 CFR 2.22 has two meanings.
* 12nm wide adjacent to territorial sea baseline for -
- 46 USC Subtitle II
- Ports and waterways safety act.
- Vessel bridge to bridge radiotelephone act
- Criminal jurisdiction pursuant to Title 18 USC
- Special maritime and territorial jurisdiction 18 USC 7
- Interpreting international law
* 3nm wide adjacent to the territorial sea baseline unless noted above.
- Territorial Sea Baseline
Defined in 33 CFR 2.20 is the mean low waterline along the coast of the Unitled States.
The territorial sea baseline in Northwestern Washington state is defined to be off Cape Flattery and then southward along the western coast. The territorial sea baseline has not been defined east of Cape Flattery and into Puget Sound. Applicability for mandatory dockside exams and carriage requirements for specific lifesaving equipment may depend on the distance from the territorial sea baseline a vessel is operating or transiting. Click to see chartlet of NW Washington.- Federal Register postings related to the CFIVS Program
- Advanced Notice of Proposed Rulemaking - Federal Register - Dec 29, 1988 - This is the advanced notice that outlines the requirements that were being considered to enact the Fishing Vessel Safety Act of 1988. Requesting comments to the proposed rules for uninspected fishing, fish tender and fish processing vessels.
- Proposed Rule - Federal Register - April 13, 1989 - - Final rule: Extension of compliance date. Originally published in the Federal Register August 17, 1988, 406 EPIRBs were required for fishing vessels operating on the high seas. Owners had until August 17, 1989 to bring their vessel in compliance, this date was extended to May 17, 1990 by this proposed rule.
- Proposed Rule - Federal Register - April 19, 1990 - This is the proposed rule to the Commercial Fishing Industry Vessel Safety (CFVIS)Act of 1988 as printed in the Federal Register for 46 CFR Part 28.
- Final Rule - Federal Register - April 19, 1990 - This is the final rule for EPIRB requirements in 46 CFR Part 25.SEC_604_FINAL
- Notice of Acceptance- Federal Register - May 24, 1990 - This notice officially recognized the Marine Index Bureau (MIB) as a qualifed party that has knowledge and experience in the collection of statistical insurance. data. The CFIVS Act required that the Coast Guard compile statisties concerning marine casualties from data compiled from insurers of commercial fishing industy vessels. The MIB was authoried to collect this informtion and make periodic reports to the Coast Guard. Since the final rule was not yet been published, insureres were encourated to begin voluntarily reporting the data to the MIB.
- Fishing Vessel Safety Act of 1988 Final Rule - Federal Register - August, 14, 1991 - This is the final rule to the Commercial Fishing Vessel Safety Act of 1988 as printed in the Federal Register proposed changes
- Supplementary Notice of Proposed Rule - Federal Register - October 27, 1992 - This SNPRM was proposed after some of the items in the Final Rule of August 14, 1991 generated comments of public concern and were separated from the final rule in order that the items could be adequately be addressed. These topic include stability for fishing vessels < 79 feet, survivall craft requirements carrying less than 4 POB inside 12 miles. Also Aleutian Trade Act, Load Lines, drill course curricula and instructor acceptance criteria, termination of fishing vessels. Register proposed changes
- Supplementary Notice of Proposedl Rule - Federal Register - January 6, 1993 - This includes corrections to SNPRM of October 27, 1992.
- Supplementary Notice of Proposedl Rule - Federal Register - September 13, 1994 - Aleutian Trade Act Vessels. Establishes proposed regulations which would allow some commercial fishing vessels to continue to proivde cargo service to remote communities in Alaska.
- Final Rule - Federal Register - October 24, 1995 - Aleutian Trade Act Vessels. New vessels are allowed to enter the trade but are required to comply with 46 CFR Part 28 subpart D. .
- Interim Rule - Federal Register - November 5, 1996 - Proposed changes to safety equipment which included revisions to 28.60 Exemption letters, 28.65 Termination of unsafe operations was being added from wording in NVIC 12-91, Table 28.120 Survival Craft, 28.225 tide and current tables, 28.270 Instructions, drills and safety orientation and 28.275 acceptance criteria for instructors and course curricula.
- Final Rule - Federal Register - September 4, 1997 - Changes to safety equipment and vessel operating requirements to the Commercial Fishing Vessel Safety Act signed Sept 15, 1991. Revisions to 28.60 Exemption letters, 28.65 Termination of unsafe operations added (b)(11) COCs for fish processing vessels, Table 28.120 Survival Craft, 28.225 added tide and current tables, 28.270 Instructions, drills and safety orientation and 28.275 acceptance criteria for instructors and course curricula.
- ANPRM - Federal Register - March 31, 2008 - Proposed changes to the Commercial Fishing Vessel Safety Regulations which include requiring stability calculations for vessels and stability training for masters of vessels between 50 and 79 feet. Changes to current requirements for immersion suits to vessel that operate beyond the boundary line and north of 32 degrees north alleviating the requirements in NVIC 1-92. Requiring a qualified drill conductor to be board vessels operating beyond the boundary line with more than 16 POB. Other changes include require registration of EPIRBs, survival craft capable of being launched by one person.
- Notice of Public Meetings - Federal Register August 12,, 2008 - Announcement of Coast Guard's intent to hold public meetings and extend comment period related to the ANPRM of March 31, 2008..
- Notice - Federal Register July 15, 2013 - Announcement of the termination of radioteleophone watchkeeping on MF frequency 2182 voice, 2187.5 DSC and 2570 weather and marine information boardcasts. This impacts documented fishing vessels that operate between 20 and 100 miles from shore. These vessels required to carry SSB 2-4 mHz which now will not be monitored for emergency distress calls. Any MF radio transmitter will not work for emergency transmissions.
- Final Rule - Federal Register - March 14, 2014 - Waiver of Citizenship Requirements
for Crewmembers on Commercial Fishing Vessels. Amendment to previous guidance as provided in HQ Policy Letter 01-02.(CANCELLED). The guidance has now been placed in the federal regulations 46 CFR Part 28. Until published in the regulations this guidance shall be utilized.- Final Rule - Federal Register - January 30, 2015- Announcement of the requirement for vessels including commercial fishing industry vessels to begin reporting of Notice of Arrivals and the requirment to carry Automatic Identification Systems (AIS). NOA required for commercial fishing industry vessels greater than 300 gross tons. AIS required for commercial fishing industry vessels 65 feet and greater.
- Notice of Proposed Rulemaking- Federal Register - June 21, 2016 - The Coast Guard proposes to align its commercial fishing industry vessel regulations with the mandatory provisions of 2010 and 2012 legislation passed by Congress that took effect upon enactment. The alignments would change the applicability of current regulations, and add new requirements for safety equipment, vessel examinations, vessel safety standards, the documentation of maintenance, and the termination of unsafe operations.
- Final Rule - Federal Register - July 22, 2016 - Harmonization of Standards for Fire Protection, Detection, and Extinguishing Equipment;
- Final Rule - Federal Register - December 06, 2024 - Harmonization of Standards for Personal Flotation Devices and carriage requirements for all vessels.
- Forms
- CG-2692 Report of Marine Casualty (Updated 3/2022).
- CG-2692B Report of Required Chemical Drug and Alcohol Testing following a Serious Marine Incident (Updated 3/2022).
- CG-2692C Personnel Casualty Addendum (Updated 3/2022).
- CG-2692D Involved Persons and Witnesses Addendum (Updated 3/2022).
- CG-5587 Commercial Fishing Vessel Safety Examination Book and Supplements - Released 05/2025, this is the checklist used by Dockside Examiners when conducting a dockside exam.
- CG-5587 Subpart D Addendum - Released 05/2025, Addendum checklist for Subpart D items (vessels with keel laid date or major conversion after 9/15/1991 and with more than 16 POB).
- CG-5587 ATA Addendum - Addendum checklist for Aleutian Trade Act Fish Tenders.
- Discontinued-5587 2008 Discontinued-5587 2019- Provided for historical purposes only.
- CG-5587B Commercial Fishing Vessel Safety Examination Supplement CG-5587B has been discontinued. All supplements are included in Form CG-5587 above.
- CG-4100F Boarding Form - This is the Boarding Officer form used for conducting boardings of commercial fishing vessels.
- HQ Safety Flyers
- Boarding Ladders (English)
- Chemical Testing (English) - (Spanish)
- Citizenship (English)
- Cold Water Survival / Hypothermia (English)
- Crew Preparedness (English) - (Spanish)
- Distress Signals (English)
- Drill Conductor (English)
- Drill Conductor A (English)
- Dockside Exams (English)
- DSC Radios (English)
- EPIRBs (English)
- Falls Overboard (English) - (Spanish)
- FCC Licenses (English)
- Fire Extinguishers (English)
- Fishing Vessel Safety Advisory Committee (English) - (Spanish)
- High Water Alarms (English)
- Hydrostatic Release Units (English)
- Icing (English)
- Maintenance Problems (English) - (Spanish)
- Modifications and Stability (English)
- Stability Training (English) - (Spanish)
- Survival Craft (English)
- Survival Equipment and Survival (English)
- Vessel Sinking (English)
- Watertight Integrity (English)
- What is a Commercial Fishing Vessel (English)
- HQ Policy Letters
- HQ Policy Ltr 14-90- Fishing Processing Vessels: Definition and Load Lines - dated Jun 20, 1990 this discusses fish processors, the requirement for them to be loadlined and discusses what types of processes qualify as processing or not..
- HQ Policy Ltr 01-96 - Excess Equipment - Excess survival equipment aboard commercial fishing vessels. Excess survival equipment can be kept on board if used for drill purposes and must be marked "for training only".
- HQ Policy Ltr 2-97 - Shore Connection - HQ determined that 1.5 inch quick disconnects are an acceptable equivalent to the standard shore connection normally required. This does not apply to oceangoing vessels 400 GT or greater on international service.
- HQ Policy Ltr 01-02- Procedures for Waiver of Requiements on Citizenship Aboard Commercial Fishing Vessels - Dated Jun 28, 2001 this provides guidance for waiving of the requirement of US citizenship aboard commercial fishing vessels.
- HQ Policy Letter 06-04 - Unspected Commercial Fishing Vessel Safety Program Management; USCG Auxiliary Examiners. - Dated July 19, 2006 this policy provides guidance for qualification and travel related to utilizing Coast Guard Auxiliary examiners for the commercial fishing vessel safety program.
- HQ Policy Ltr 04-07 - Acceptance of 3rd Party Organizations - Dated Aug 6, 2007provided additional guidance on the acceptance of accepted organization and similarly qualified organizations and provided for rescinding of acceptance of an individual third party qualification. This guidance also stipulates that all exam paperwork be submitted to the Area Coordinators as opposed to District as outlined in 46 CFR 28.710(e).
- HQ Policy Ltr 04-08 - Unserviceable Survival Equipment- dated 6 August 2004 provides guidance on what should be done with unserviceable survival equipment on board commercial fishing vessels. Also discusses termination guidance for survival craft 5 months beyond service date, hydrostatic releases and disposable hydrostatic release units 5 months past expiration. An inflatable survival craft that is beyond its servicing date by 5 months must be removed from the vessel and surviced. Inflatable survival craft may not be kept on board and marked for drill use only, even if it is not required due to the vessels route.
- HQ Policy Ltr 11-11 - Engineering Officer Endorsements on uninspected fishing vessels dated 7 Oct 2011. Provides criteria for each level of engineering officer.
- HQ Policy Letter 12-02 - CFV Safety Program Management: USCG Auxiliary CFV Examiner and Dockwalking Augumenation. - Dated March 1, 2012 - FInal policy that states that Coast Guard Auxiliary personnel may assist the CFIVS program by conducting mandatory dockside exams as proviided for with the signing of the Coast Guard Authorization Act of 2010.
- HQ Policy Letter 13-01 - Interum Guidance for Revised MARPOL Annex V Implementation - Dated February 26, 2013 - Changes to the Marine Pollution (MARPOL) international convention took affect January 1, 2013. this provides guidance on implementing these changes until Federal Regulations can be updated.
- HQ Policy Letter 15-05 - Replacements for out of the water survival craft and replacement of life floats and rigid buoyant apparatus- Dated December 15, 2015 - As of February 26, 2016 vessels that were required to carry a life float or a rigid buoyant apparatus must be replaced with suvival craft that does not allow any part of a persons body to be immersed in water. This would require at least an inflatable buoyant apparatus or any inflatable life raft..
NVICs NVIC 7-68 - Notes on Inspection and Repair of Steel Hull NVIC 1-83 - Painter line for buoyant apparatus and life floats NVIC 4-86 - Hydrostatic Release Units and Alternate Float Free Arrangements NVIC 5-86 - Voluntary Standards for U.S. Uninspected Commercial Fishing Vessels - Before the passing of the Commercial Fishing Vessel Safety Act of 1988 this NVIC was released as voluntary safety equipment recommendations for commercial fishing vessels, compliance was voluntary. THIS IS PROVIDED AS HISTORICAL INFORMATION. NVIC 1-87 - Retroreflective Material Installation NVIC 8-87 - Notes on Design, Construction, Inspection and Repair of Fiber Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Vessels NVIC 7-91 - Determination of Cold water areas - All waters in the Northwest District are cold waters. NVIC 12-91 - Termination of Unsafe Operations Aboard Commercial Fishing Industry Vessels - This was initial guidance from HQ on termination for commercial fishing vessels. This has some good verbiage on the general stance on when terminations might be appropriate. NVIC 13-91 Change 1 - Dated Apr 28, 1993 this provided initial policy for 3rd party organizations and established criteria for "accepted organizations" and "similarly qualified organizations". NVIC 1-92 Implemention of Life Saving Equipment Requirements - dated 4 Feb 1992, initial guidance which replaced NVIC 1-92 Change 1 - dated 2 Aug 1992, this NVIC clarifies regulations and policies concerning inflatable life rafts. Use of non-SOLAS approved for applications where 4 person life raft is allowed. NVIC 1-92 Change 2 - dated 4 Mar 1994, this NVIC temporarily revised the allowed carrying capacity of certain unapproved inflatable liferafts for commecial fishing vessels. This expired January 1, 1999. THIS IS PROVIDED AS HISTORICAL INFORMATION. NVIC 7-93 Guidelines for Drill Instructor Courses - dated Aug 24, 1993, this provides guidance for accepting course curriculum for the training of Drill Instructors who are then qualified to teach Drill Conductors how to conduct drills aboard commercial fishing vessels. NVIC 7-95 - Guidance on Inspection, Repair and Maintenance of Wooden Hulls NVIC 3-99 - GMDSS Requirements - Provides guidance for what GMDSS equipment is required for vessels. NVIC 7-01 - Procedures for Hull Inspection and Repair on Vessel Built of Riveted Construction NVIC 8-04 - Guide To Marine Equipment Approvals Covered by US-EC MAR- provides guidance on the Agreement between the United States and the European Community on mutual recognition of certificates of conformance. This allows the Coast Guard to accept equipment approved by the EC as we currently accept SOLAS approved equipment. See NVIC 02-19 and NVIC 02-19 Change 1 below. THIS IS PROVIDED AS HISTORICAL INFORMATION
NVIC 1-08 - Testing of Immersion Suits- dated 28 Jan 2008 - provides recommended testing intervals for leak testing seams and closures.
(Note that this is not a legal requirement nor is it a rule. If during an inspection the condition of the immersion suit is in question due to the material condition of the suit, the owner may elect to have the suit tested as per this NVIC in order to prove its condition as being satisfactory.)NVIC 3-14 - Guidelines for Organizations offering CG approved courses - dated January 22, 2014, this provides approval requirements for organizations that offer Coast Guard approved courses. NVIC 01-16 Change 3 - Equivalency Determination for Chart and Publication Carriage - dated August 18, 2025, this circular describes equivalencies for electronic charts, electronic publications, and ENC-derived paper charts in lieu of the carriage requirements found in regulations and to provide procedures for conducting inspections for vessels electing to comply with one or more of the equivalencies described. NVIC 02-19 - Guide to Marine Equipment Approval covered by a Mutual Recognition Agreement (MRA) - dated November 1, 2019, this document supersedes and cancels Navigation and Vessel Inspection Circular(NVIC). 8-04, listed above and provides guidance on the parallel agreements the United States of America (US) has with the European Community (EC) and with the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) countries which are part of the European Economic Area (EEA) on the Mutual Recognition of Certificates of Conformity for Marine Equipment NVIC 02-19 Change 1 - Guide to Marine Equipment Approval covered by a Mutual Recognition Agreement (MRA) - dated January 1, 2021. This MRA is parallel to the previously signed MRAs between the US and the European Community (EC), and the US and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) countries, which are part of the European Economic Area (EEA). Paragraph 6. lists the changes to the previous NVIC. Placards Phone List of CFIVS Contacts for All Districts Program Guidance (Post 2010, 2012 & 2015 Auth Acts)
- 2010 Mandatory Dockside Exams
- Coast Guard Authorization Act of 2010 - This is an excerpt from the law (section 604) which relates to legislation that changes the voluntary nature of the CFIVS Program to mandatory examinations for vessels that operate beyond 3 nautical miles from the territorial sea baseline. It also alleviates the boundary line for the above 3nm line. Many other safety equipment changes.
- Mandatory Exam Letter to the Fishing Industry - Dated August 15, 2012 this is the letter to the commercial fishing industry notifying them of the requirement to get a mandatory dockside exam.
- HQ Guidance Document - Released on 23 October 2012 provides definitions for "build date" and "substantial change", althernate safety compliance programs and dockside examinations.
- 2012 Changes to Mandatory Dockside Exams
- Coast Guard and Maritime Transportation Act of 2012 language - Dated Dec 20th, 2012. The applicable text has been highlighted for easy viewing by our folks if they would like to view the language.
-- in the reqts for mandatory dockside exams, replaces the wording and requires vessel complete the first dockside exam before Oct 15, 2015.
- in the reqts for mandatory dockside exams, replaces the wording "at least once every two years" with "at least once every five years." It adds wording that requires completion of the first dockside examination not later than October 15, 2015.
-- in the reqts for class certification for new builds over 50 ft, replaces the July 2012 date with July 2013 instead.
-- same for loadline reqts for new builds over 79 ft.
-- in the alternate safety compliance reqts, replaces the July 2012 date cutoff for major conversions with July 2013.
-- defines the term "built."
-- modifies the sunset date for buoyant apparatus and lifefloats to a future date (at least 2016) dictated by completion of a report to Congress on the effectiveness of such survival craft.- US Code Changes from 2012 Auth Act - This document is a copy of US Code which currently includes language changes from the 2010 Auth Act to sections 4502, 4503, 5102 and 5103. Corrections as per The 2012 Auth Act have been pen and inked into this document in red.
- Mandatory Exam Letter to fishing industry - Dated 18 August 2015.
- Marine Safety Information Bulletin - Dated 1 December 2014 purpose to remind the comercial fishing industry changes by Coast Guard Authorization Act of 2010 and the Coast Guard and Maritime Transportation Act of 2012. Includes information on mandatory exams, survival craft no longer allowed where any part of the body cannot be immersed in water, definition of the term "built", load lines, and alternate safety compliance programs.
- 2015 Changes to Classification
- Coast Guard Auth Act of 2015 language - Dated Feb 8, 2016. The applicable text has been highlighted for easy viewing.
-- Vessels at least 50 feet but not more than 79 feet, constructed after Feb 8, 2016 must be designed by an individual licensed by a State as a naval architect or marine engineer, and the design incorporates standards equivalent to those prescribed by a classification society accepted by the Secretary.
-- Construction of the vessel is overseen and certified
as being in accordance with its design by a marine surveyor
of an organization accepted by the Secretary.
Reports
- Living to Fish - Dying to Fish - In a three-week period at the dawn of 1999, eleven lives and four clam/conch fishing vessels were lost off the mid-Atlantic coast. This quick succession of casualties in one fishery, in a small geographic area, shocked the regional fishing community. Questions were raised as to whether they represented a statistical anomaly or a worsening trend in fishing safety. Rear Admiral Robert C. North, the Coast Guard’s Assistant Commandant for Marine Safety and Environmental Protection, chartered a Task Force to:
1. evaluate recent serious casualties;
2. examine recent casualties in the context of historical data;
3. provide quick feedback to the industry;
4. review the current fishing vessel safety program and past safety initiatives;
5. recommend significant measures to reduce loss of life and vessels; and,
6. develop direction for government and industry.The Task Force was chartered on 27 January 1999 and this report was due to Admiral North on 19 March 1999. The charter is in Appendix A.
- Analysis of Fishing Vessel Casualties - Conducted by the HQ Office of Investigations and Analysis, Compliance and Analysis Division, dated December 2011. This is a review of Fishing Vessel Casualties from 1992 to 2010.
Regulations (Code of Federal Regulations (CFR))
- 46 CFR Part 28 - Requirements for Commerical Fishing Industry Vessels
- Subpart A - General Provisions
- Subpart B - Requirements for all Vessels
- 28.100 - Applicability
- 28.105 - Life Saving Equipment - General Requirements
- 28.110 - Life Preservers or Other Personal Flotation Devices
- 28.115 - Ring Life Buoys
- 28.120 - Survival Craft
- 28.125 - Stowage of Survival Craft
- 28.130 - Survival Craft Equipment
- 28.135 - Lifesaving Equipment and Markings
- 28.140 - Operational readiness, maintenance, and Inspection of Lifesaving Equipment
- 28.140(d) - Escape Routes Unobstructed
- 28.145 - Distress Signals
- 28.150 - Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacons (EPRIBs)
- 28.155 - Excess Fire Detection and Protection Equipment
- 28.160 - Portable Fire Extinguishers (Vessels 65 feet or greater)
- 28.165 - Injury Placard
- Subpart C - Documented Vessels That Operate Beyond the Boundary Line or With More Than 16 Individuals on Board or Fish Tender Vessels Engaged in the Aleutian Trade.
- 28.200 - Applicabilty
- 28.205 - Fireman's Outfits / Self-contained Breathing Apparatus
- 28.210 - First Aid Equipment and Training
- 28.215 - Guards for Exposed Hazardous
- 28.225 - Navigation Information
- 28.230 - Compasses
- 28.235 - Anchors / Radar Reflectors
- 28.240 - General Alarm System
- 28.245 - Communication Equipment
- 28.250 - High Water Alarms (Vessels greater than 36 feet)
- 28.255 - Bilge Pumps, Bilge Piping and Dewatering Systems
- 28.260 - Electronic Position Fixing Device
- 28.265 - Emergency Instructions
- 28.270 - Instructions Drill and Safety Orientation
- 28.275 - Acceptable Criteria for Instuctors and Course Curricula
- Subpart D - Vessels Built / Keel Laid / Converted on or After Sept 15, 1991 That Operates With More Than 16 Individuals on Board
- 28.300 - Applicabilty and General Requirements
- 28.305 - Life Saving and Signaling Equipment
- 28.310 - Launching of Survival Craft
- 28.315 - Fire Pumps, Fire Mains, Fire Hydrants and Fire Hoses
- 28.320 - Fixed Gas Fire Extinguishing Systems
- 28.325 - Fire Detection Systems
- 28.330 - Galley Hood and Other Fire Protection Equipment
- 28.335 - Fuel Systems
- 28.340 - Ventilation of Enclosed Engine and Fuel Tank Spaces
- 28.345 - Electrical Standards (Vessels less than 79 feet)
- 28.350 - General Requirements for Electrical Systems
- 28.355 - Main Source of Electrical Power
- 28.360 - Electrical Distribution Systems
- 28.365 - Overcurrent Protection and Switched Circuits
- 28.370 - Wiring Methods and Materials
- 28.375 - Emeregnecy Source of Electrical Power
- 28.380 - General Structual Fire Protection
- 28.385 - Structural Fire Protection (Vessels with greater than 40 Individuals on Board)
- 28.390 - Means of Escape
- 28.395 - Embarkation Stations
- 28.400 - Radar and Depth Sounding Devices
- 28.405 - Hydraulic Equipment
- 28.410 - Deck Rails, Lifelines, storm rails, and hand grabs
- Subpart E - Stability
- 28.500 - Applicability
- 28.501 - Substantial Alterations
- 28.505 - Vessel Owner's Responsibility
- 28.510 - Definition of Stability Terms
- 28.515 - Submergence Test as an Alternative to Stability Calculations
- 28.530 - Stability Instructions
- 28.535 - Inclining Test
- 28.540 - Free Surface
- 28.545 - Intact Stability When Using Lifting Gear
- 28.550 - Icing
- 28.555 - Freeing Ports
- 28.560 - Watertight and Weathertight Integrity
- 28.565 - Water on Deck
- 28.570 - Intact Righting Energy
- 28.575 - Severe Wind and Roll
- 28.580 - Unintentional Flooding
- Subpart F - Fish Processing Vessels
- Subpart G - Aleutian Trade Act Vessels
- 28.800 - Applicability and General Requirements
- 28.805 - Launching of Survival Craft
- 28.810 - Deck, Rails, Lifelines, Storm Rails adn Hand Grabs
- 28.815 - Bilge Pumps, Bilge Piping, and Dewatering Systems
- 28.820 - Fire Pumps, Fire Mains, Fire Hydrants, and Fire Hoses
- 28.825 - Excess Fire Detection and Protection Equipment
- 28.830 - Fire Detection Systems
- 28.835 - Fuel Systems
- 28.840 - Means for Stopping Pumps, Ventilation, and Machinery
- 28.845 - General Requirements for Electrical Systems
- 28.850 - Main Source of Electrical Power
- 28.855 - Electrical Distribution Systems
- 28.860 - Overcurrent Protection and Switch Circuits
- 28.865 - Wiring Methods and Materials
- 28.870 - Emergency Source of Electrical Power
- 28.875 - Radar, Depth Sounding, and Auto-pilot
- 28.880 - Hydraulic Equipment
- 28.885 - Cargo Gear
- 28.890 - Examination and Certification of Compliance
- 28.895 - Loadlines
- 28.900 - Post Accident Inspection
- 28.905 - Repairs and Alterations
- 46 CFR Part 25 - Uninspected Vessel Requirements
- 25.25 - Life Preservers and Other LifeSaving Equipment
- 25.26 - Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacons (EPIRBS)
- 25.30-15 - Fixed Fire Extinguishing Systems
- 25.30-40 - Fire Extinguishing Equipment Requirements (Vessels less than 65 feet)
- 25.35 - Backfire Flame Arrestors (Gasoline powered inboard engines)
- 25.40 - Ventilation Systems
- 25.50 - Garbage Retention
- 26.30 - Work Vests
- 25 CFR Part 249- Fish and Wildlife - Off Reservation Treaty Fishing (Bureau of Indian Affairs)
- 249.7 - Saving Provisions (Enforcement of safety and navigation laws)
- 33 CFR Part 26 - Vessel Bridge To Bridge Radiotelephone Regulations
- 26.03 - Radiotelephone Required
- 33 CFR Part 88 - Pilot Rules
- 88.05 - Copy of Nav Rules (Requirement to Carry on Inland Waters)
- 33 CFR Part 138 - Financial Responsibility for Water Pollution (Vessels)
- 138.15(a)(2) - Applicability (Not required for vessel 300 gross tons and less)
- 33 CFR Part 151 - Vessels Carrying Oil, Noxious Liquid Substances, Garbage
- 151.10 - Control of Oil Discharges
- 151.19 - International Oil Pollution Prevention (IOPP) Certificates
- 151.25 - Oil Record Books
- 151.26 - Shipboard Oil Pollution Emergency Plan
- 151.55 - Recordkeeping Requirements
- 151.57 - Waste Management Plans
- 151.59 - Placards
- 151.63 - Shipboard Control of Garbage
- 33 CFR Part 154 - Facilities Transferring Oil or Hazardous Material in Bulk (250 barrels or more)
- 154.500 - Hose Assemblies
- 33 CFR Part 155 - Oil or Hazardous Material Pollution Prevention Regulations for Vessels
- 155.100 - Applicability
- 155.120 - Equivalents
- 155.320 - Fuel Oil Containment (in case of spill)
- 155.330 - Bilge Slops Containment - non ocean going ships
- 155.350 - Bilge Slops Containment - Oceangoing Ships less then 400 Gross Tons
- 155.360 - Bilge Slops Containment - Oceangoing Ships Greater than 400 Gross Tons less than 10,000 Gross Tons
- 155.370 - Bilge Slops Containment - Oceangoing Ships Greater than 10,000 Gross Tons or Greater then 400 that Carries Ballast in Fuel Tanks
- 155.410(a)(3) - Pumping, Piping and Discharge Requirements - non ocean going ships 100 Gross Tons and above
- 155.420(a)(3) - Pumping, Piping and Discharge Requirements - Oceangoing Ships Greater than 100 and less than 400 Gross Tons and above
- 155.430 - Standard Discharge Connections for Oceangoing ships of 400 Gross Tons and above
- 155.450 - Placard
- 155.470 - Prohibited Spaces
- 155.700 - Designation of Person in Charge of Transfer Operations
- 155.710 - Contents of Letter of Designation
- 155.715 - Contents of Letter of Designation
- 155.720 - Transfer Procedures
- 155.730 - Compliance with Transfer Procedures
- 155.740 - Availablity of Transfer Procecedures
- 155.750 - Contents of Transfer Proceduresxx
- 155.785 - Communications
- 155.790 - Deck Lighting
- 155.800 - Transfer Hose
- 155.805 - Closure Devices
- 155.820 - Records
- 33 CFR Part 159 - Marine Sanitation Devices
- 33 CFR Part 161 - Navigation Safety Regulations
- 46 CFR Part 7- Boundary Lines of the United States
- 7.1 - General Purpose of Boundary Lines.
- 7.5 - Rules for Establishing BoundaryLlines
- 7.5(c) - Generic Definition of the Boundary Line
- Atlantic Coast
- 7.10 - Eastport, ME to Cape Ann, MA
- 7.15 - Massachusetts Bay, MA
- 7.20 - Nantucket Sound, Vineyard Sound, Buzzards Bay, Narragansett Bay, MA, Block Island Sound and Easterly Entrance
- 7.25 - Montauk Point, NY to Atlantic Beach, NY
- 7.30 - New York Harbor, NY
- 7.35 - Sandy Hook, NJ to Cape May, NJ
- 7.40 - Delaware Bay and Tributaries
- 7.45 - Cape Henlopen, DE to Cape Charles, VA
- 7.50 - Chesapake Bay and Tributaries
- 7.55 - Cape Henry, VA to Cape Fear, NC
- 7.60 - Cape Fear,NC to Sullivans Island, SC
- 7.65 - Charleston Harbor, SC
- 7.70 - Foley Island, SC to Hilton Head, SC
- 7.75 - Savanna River / Tybee Roads
- 7.80 - Tybee Island, GA to St Simons Island, GA
- 7.85 - St. Simons Island, GA to Little Talbot Island, FL
- 7.90 - St, Johns River, FL
- 7.95 - St, Johns Point, FL to Miami Beach, FL
- 7.100 - Florida Reefs and Keyes from Miami, FL to Marquesas Keys, FL
- Gulf Coast
- 7.105 - Marquesas Keys, FL to Rio Grande, TX
- Hawaii
- 7.110 - Mamala Bay, HI
- Pacific Coast
- 7.115 - Santa Catalina Island, CA
- 7.120 - Mexican / United States Boarder to Point Fermin, CA
- 7.125 - Point Vincente, CA to Point Conception, CA
- 7.130 - Point Conception, CA to Point Sur, CA
- 7.135 - Point Sur, CA to Cape Blanco, OR
- 7.140 - Cape Blanco, OR to Cape Flatery, WA
- 7.145 - Strait of Juan de Fuca, Haro Stait to Georgia, WA
- Alaska
- 7.150 - Canadian (BC) and United States (AK) Boarders to Cape Spencer, AK
- 7.155 - Cape Spencer, AK to Cape St. Elias, AK
- 7.160 - Point Whitshed, AK to Aialik Cap, AK
- 7.165 - Kenai Peninsula, AK to Kodiak Island, AK
- 7.170 - Alaska Peninsula, AK to Aleutian Islands, AK
- 7.175 - Alaska Peninsula, AK to Nunivak, AK
- 7.180 - Kotzebue Sound, AK
- 47 CFR Part 80 - Stations in Maritime Service (FCC - Telecommunications)
Safety Recall Notices US Code
- 46 USC 2101 - Definitions
- 46 USC 2102 - Aleutian Trade definition
- 46 USC 3302 - Part time tenders & Exemption from inspections
- 46 USC 3304(d) - Carrying passengers in addition to the crew
- 46 USC 3702(c) - Carrying bulk hazardous cargoes
- 46 USC 4502 - Vessel Safety Standards (includes 2010 and 2012 changes)
- 46 USC 4503 - Fishing, tender, and processing vessels (includes 2010 and 2012 changes)
- 46 USC 4505 - Terminations
- 46 USC 4506 - Granting exemptions
- 46 USC 5102 - Loadline application (includes 2010 and 2012 changes)
- 46 USC 5103 - Loadline assignments (includes 2010 and 2012 changes)
- 46 USC 8103 - Citizenship of officers/masters
- 46 USC 8104 - Watches
- 46 USC 8105 - Exemption from STCW
- 46 USC 8304 - Officer licensing requirement
- 46 USC 10101 - Definition of Seaman
- 46 USC 10601 - Crew contracts
- 46 USC 11101 - Accommodations for Seaman
- 46 USC 12131 - Command of Documented Vessels
- 46 USC 12135 - Invalidation of Certificates of Documentation